The overarching objective of calculating the contribution margin is to figure out how to improve operating efficiency by lowering each product’s variable costs, which collectively contributes to higher profitability. To calculate the contribution margin, we must deduct the variable cost per unit from the price per unit. For a quick example to illustrate the concept, suppose there is an e-commerce retailer selling t-shirts online for $25.00 with variable costs of $10.00 per unit. The contribution margin is the amount of revenue in excess of variable costs. One way to express it is on a per-unit basis, such as standard price (SP) per unit less variable cost per unit. The contribution margin helps analyze the impact of changes in sales volume, pricing, or costs on profitability and assists in making informed decisions regarding product mix, pricing strategies, and resource allocation.
Contribution Margin Ratio:
Recall that Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting explained the characteristics of fixed and variable costs and introduced the basics of cost behavior. The company will use this “margin” to cover fixed expenses and hopefully to provide a profit. In our example, if the students sold \(100\) shirts, assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), the total variable costs would be \(\$1,000\) (\(100 × \$10\)). If they sold \(250\) shirts, again assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), then the total variable costs would \(\$2,500 (250 × \$10)\). When only one product is being sold, the concept can also be used to estimate the number of units that must be sold so that a business as a whole can break even. For example, if a business has $10,000 of fixed costs and each unit sold generates a contribution margin of $5, the company must sell 2,000 units in order to break even.
- In fact, we can create a specialized income statement called a contribution margin income statement to determine how changes in sales volume impact the bottom line.
- To get the ratio, all you need to do is divide the contribution margin by the total revenue.
- We will discuss how to use the concepts of fixed and variable costs and their relationship to profit to determine the sales needed to break even or to reach a desired profit.
- Let’s take another contribution margin example and say that a firm’s fixed expenses are $100,000.
How to calculate the contribution margin and the contribution margin ratio?

You will also learn how to plan for changes in selling price or costs, whether a single product, multiple products, or services are involved. The Contribution Margin Ratio is a measure of profitability that indicates how much each sales dollar contributes to covering fixed costs and producing profits. It is calculated by dividing the contribution margin per unit by the selling price per unit. Contribution margin income statement, the output of the variable costing is useful in making cost-volume-profit decisions.
Formula and Calculation of Contribution Margin
The contribution margin is given as a currency, while the ratio is presented as a percentage. For instance, in Year 0, we use the following formula to arrive at a contribution margin of $60.00 per unit. If the contribution margin is too low, the current price point may need to be reconsidered. In such cases, the price of the product should be adjusted for the offering to be economically viable. The same percentage results regardless of whether total or per unit amounts are used. Soundarya Jayaraman is a Content Marketing Specialist at G2, focusing on cybersecurity.
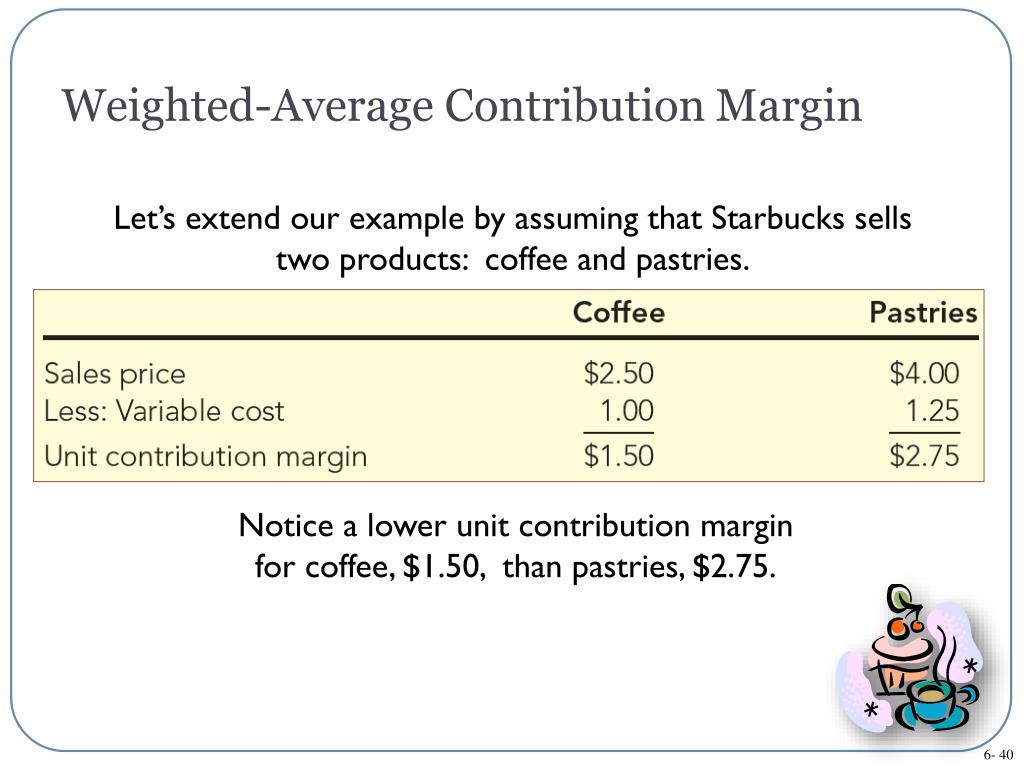
Likewise, a cafe owner needs things like coffee and pastries to sell to visitors. The more customers she serves, the more food and beverages she must buy. These costs would be included when calculating the contribution margin.
Contribution Margin Formula Components
It is an important input in calculation of breakeven point, i.e. the sales level (in units and/or dollars) at which a company makes zero profit. Breakeven point (in units) equals total fixed costs divided by contribution margin per unit and breakeven point (in dollars) equals total fixed costs divided by contribution margin ratio. For the month of April, sales from the Blue Jay Model contributed $36,000 toward fixed costs. Looking at contribution margin what is a note payable definition nature example and journal entries in total allows managers to evaluate whether a particular product is profitable and how the sales revenue from that product contributes to the overall profitability of the company. In fact, we can create a specialized income statement called a contribution margin income statement to determine how changes in sales volume impact the bottom line. For the month of April, sales from the Blue Jay Model contributed \(\$36,000\) toward fixed costs.
Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. Find out what a contribution margin is, why it is important, and how to calculate it.
Weighted average contribution margin ratio equals the sum of contribution margins of all products divided by total sales. The CVP relationships of many organizations have become more complex recently because many labor-intensive jobs have been replaced by or supplemented with technology, changing both fixed and variable costs. For those organizations that are still labor-intensive, the labor costs tend to be variable costs, since at higher levels of activity there will be a demand for more labor usage. A higher contribution margin indicates a higher proportion of revenue available to cover fixed costs and contribute to profit. Break even point (BEP) refers to the activity level at which total revenue equals total cost.
Variable costs are those costs that change as and when there is a change in the sale. An increase of 10 % in sales results in an increase of 10% in variable costs. High CM ratios are generally desirable because they indicate that a large portion of each sale contributes to covering fixed costs and profit. However, it is also essential to balance this with the level of fixed costs – a business with high fixed costs will need a higher CM ratio to break even. It provides one way to show the profit potential of a particular product offered by a company and shows the portion of sales that helps to cover the company’s fixed costs.